
Quartz sand is an important industrial mineral raw material, widely used in glass, ceramics, casting, chemical industry and other fields. However, natural quartz sand usually contains various impurities, such as calcium, iron, aluminum, etc., which will affect the quality and application performance of quartz sand. Therefore, removing impurities in quartz sand and improving the purity of quartz sand are key links in the quartz sand processing process. This article will focus on the removal of calcium impurities in quartz sand.
For the removal of calcium impurities, there are several common quartz sand purification methods, including scrubbing, acid leaching, flotation, magnetic separation, chemical purification and high-temperature calcination.

The scrubbing method uses mechanical force and friction to remove impurities and films on the surface of quartz sand, thereby improving the purity of quartz sand. During the scrubbing process, the quartz sand particles rub and collide with each other, causing impurities to fall off the surface of the quartz sand. At the same time, adding an appropriate amount of water can play a role in lubrication and dispersion, improving the scrubbing effect.
Generally, the scrubbing time ranges from tens of minutes to several hours, depending on the properties of the quartz sand and the impurity content. After the scrubbing process, the quartz sand is discharged from the scrubber, dehydrated and dried to obtain a purified quartz sand product.

The acid leaching method uses acid to react with calcium and other impurities in quartz sand to dissolve the impurities in the acid solution, thereby achieving the purpose of removing impurities. Commonly used acids include hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, etc. After the ore is crushed to a certain particle size, the quartz sand particles are added to the acid solution and acid leached under certain temperature and stirring conditions. The acid leaching time generally ranges from a few hours to dozens of hours, depending on the properties of the quartz sand and the impurity content. After the acid leaching treatment, the quartz sand is separated from the acid solution and washed with clean water to remove residual acid and dissolved impurities.

Flotation is a mineral processing method that utilizes the differences in the physical and chemical properties of the mineral surface and adds flotation agents to make the target minerals selectively attach to the bubbles, thereby achieving mineral separation. For calcium impurities in quartz sand, reverse flotation is usually used, that is, adding inhibitors to inhibit the floating of quartz sand, and adding collectors to make impurity minerals such as calcium float, so as to achieve the separation of quartz sand and calcium impurities.
When the minerals are in a monomer dissociation state, they are added to the flotation machine, and inhibitors and collectors are added for flotation treatment. During the flotation process, impurity minerals such as calcium are adsorbed by the flotation agent, attached to the bubbles and float to the surface of the pulp, forming a foam product, while the quartz sand remains in the pulp and becomes tailings.

Magnetic separation is a mineral processing method that uses the magnetic difference of minerals to separate magnetic minerals from non-magnetic minerals through the action of a magnetic field. Magnetic impurities such as iron in quartz sand can be removed by magnetic separation. Under the action of the magnetic field, magnetic impurities such as iron are adsorbed on the drum of the magnetic separator, while quartz sand is not affected by the magnetic field and is discharged from the magnetic separator, thereby separating quartz sand from magnetic impurities.
The magnetic field strength and number of magnetic separations of the magnetic separator can be adjusted according to the properties of the quartz sand and the impurity content. After magnetic separation, the quartz sand is discharged from the magnetic separator to obtain a quartz sand product after the magnetic impurities are removed.

Chemical purification is to remove impurities from quartz sand by using the principle of chemical reaction. Commonly used chemical purification methods include acid leaching, alkali leaching, chlorination, etc. The process flow of chemical purification is similar to that of acid leaching to remove calcium impurities. The obtained qualified particle size mineral particles are added to the chemical solution and chemically reacted under certain temperature and stirring conditions. After the reaction treatment, the quartz sand is separated from the chemical solution and washed with clean water to remove the residual chemical solution and dissolved impurities. Finally, the washed quartz sand is dried to obtain the purified quartz sand product.
The high-temperature calcination method uses the physical and chemical changes of quartz sand at high temperatures to remove impurities and moisture in quartz sand, thereby improving the purity of quartz sand. At high temperatures, impurities in quartz sand will decompose, volatilize or react chemically with quartz sand, thereby being removed. At the same time, high-temperature calcination can also make the crystal structure of quartz sand more compact, improve the hardness and high-temperature resistance of quartz sand.
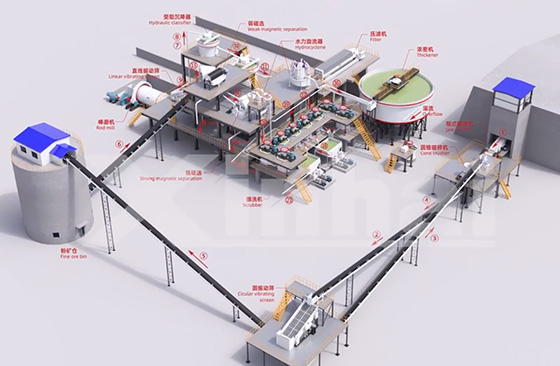
The removal of calcium impurities in quartz sand and the purification of quartz sand are key links to improve the quality and application performance of quartz sand. Each method has its own unique principles and process flow. In practical applications, it is necessary to select appropriate purification methods and process flows according to the properties and impurity content of quartz sand to achieve a reasonable purification effect. At the same time, it is also necessary to strengthen the control and management of the purification process, improve purification efficiency and product quality, and reduce production costs and environmental pollution.
To find out more about our products and solutions, please fill out the form below and one of our experts will get back to you shortly.