
Compared with the flotation of sulfide minerals, the flotation of non-sulfide minerals is more difficult. The non-sulfide minerals usually have a higher water solubility, and the useful minerals and gangue minerals are usually similar types, with a small difference in surface properties. So, what should be noticed in the flotation separation of non-sulfide minerals?
The common non-sulfide minerals include various oxidized minerals, alkaline earth metal minerals, aluminosilicate and soluble salts, such as tungsten ore, (titanium) iron ore, malachite and calamine. In the flotation separation of non-sulfide minerals, we can interpret the commonness and characteristics of non-sulfide minerals flotation from the aspects of the properties of the non-sulfide mineral and the selected flotation reagents, so as to better float the non-sulfide minerals.
Due to the small difference in surface properties between useful minerals and gangue minerals, the flotation separation is difficult, so it is necessary to maximize the difference in surface properties between useful minerals and gangue minerals. Here are several aspects that we can consider to change the differences in mineral surface properties, such as pH value, the reaction time of flotation reagent, agitation strength, water quality and temperature at each stage.

Taking the temperature as an example, we can improve the buoyancy of useful minerals or increase the inhibition of gangue minerals by adjusting the temperature. For example, when the collector of fatty acid is used to float fluorite and the pulp temperature is in the range of 5~35 degrees, the recovery rate of fluorite is gradually increased but the increasing speed of recovery rate is gradually decreased. When the scheelite is floated, high temperature can improve the inhibition ability of sodium silicate to calcite and fluorite.
In addition, non-sulfide minerals usually need a more complex pulp preparation process before the flotation separation, which includes scrubbing, desliming, heating and mixing, and agitation with the high concentration.

Among them, desliming is a common and key operation. The fine mud produced from the non-sulfide minerals will consume the flotation reagent and adhere to the surface of coarse particles, then interfering the separation process. Some fine mud may also contain a large number of useful minerals, so sometimes the desliming material is divided into coarse and fine grains for treatment.
When selecting the flotation reagents for non-sulfide minerals, we should select different regulators and collectors for different minerals.
For example, the sodium silicate and ferrous sulfate are used to inhibit chlorite and carbonate, the sodium silicate is used to inhibit calcite and mica, the sodium sulfide and sodium carbonate are adopted to inhibit calcium magnesium carbonate.

The non-sulfide mineral collectors are divided into anionic collectors and cation collectors.
Anionic collectors include fatty acids, hydrocarbon sulfonates, sulfovinate, which are mainly used for flotation separation of tungsten and tin, as well as the non-metallic minerals.
Cation collectors include nitrogenous monoamines and quaternary ammonium compounds, which are mainly used for flotation separation of iron ore, quartz, silicate and other minerals.

Among them, the common collectors mainly include fatty acids, amines and petroleum sulfonates. Other collectors also include alkyl fatty acid salt, sulfonated succinate, alkyl acid hydrochloric acid, phosphonic acid and amphoteric collector.

Taking the scheelite as an example, the phosphate and sodium silicate are often used as the regulators in the flotation separation process, fatty acid and sulfonic acid or amine collector are used as the collector.
The above are some problems need to be noticed in flotation separation of non-sulfide minerals. There are many kinds of non-sulfide minerals, and there are some problems need to be noticed for each kind of non-sulfide minerals. It is suggested to entrust qualified mineral processing laboratory or mineral processing equipment manufacturer to carry out mineral processing test, and determine the technological process and reagent system according to ore properties.
Burma lead-zinc oxide mineral processing test
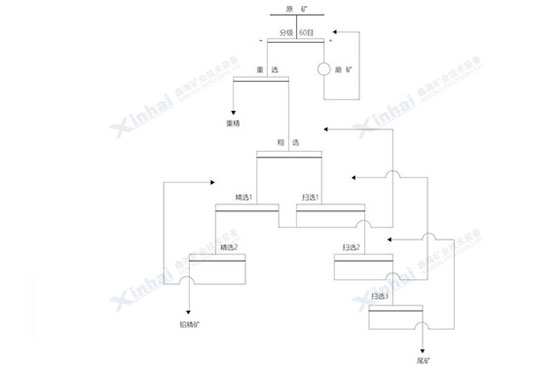
Mineral properties: The lead content was 23.39%, and its oxidation rate was as high as 75.72%.The main metallic minerals in the mine were white lead, limonite, hematite and pyroxene, and the main non-metallic minerals were quartz, feldspar, amphibole, chlorite, calcite, mica and some clay minerals.
Xinhai solution: According to the characteristics of the ore, Xinhai adopted the combined process of gravity separation and flotation process, which was featured with the simple flow and fewer kinds of reagents. After the gravity separation process, the lead concentrate with a grade of 50.3% and the recovery rate of 50.14% was obtained. The tailings were put into the flotation operation. After one roughing, two scavengings and three cleanings, the lead concentrate with a grade of 55.00% and the recovery rate of 24.59% was obtained. Taken together, the grade of lead concentrate was 53.69% and the recovery rate was 74.73%.
To find out more about our products and solutions, please fill out the form below and one of our experts will get back to you shortly.