
High Purity Quartz Sand (HPQ) has emerged as a strategic raw material underpinning the rapid advancement of high-tech manufacturing. Driven by robust growth in industries such as semiconductors, photovoltaics, and high-performance glass, the global high-purity quartz sand market is poised for sustained expansion. Unlike conventional quartz sand, HPQ demands extremely stringent control over chemical impurities and processing conditions, making it one of the most technically demanding industrial minerals.
Starting from practical applications, this article will explore how high purity quartz sand is refined, focusing on the key technical links that need to be controlled. It will also conduct a comparison between high purity quartz sand from different regions and finally examine the future development direction of this industry.
HPQ refers to quartz materials with extremely high silicon dioxide (SiO₂) content (usually exceeding 99.99%) and extremely low levels of impurities such as iron, aluminum, titanium, lithium, and boron. Based on application requirements, HPQ products are typically classified into 4N, 5N, or even higher purity grades.

High purity quartz sand vs regular quartz sand: Compared with regular quartz sand used in construction or ordinary glass production, HPQ exhibits significant advantages in chemical stability, heat resistance, and optical properties. Regular quartz sand usually contains high concentrations of trace elements and mineral inclusions, which are unacceptable in semiconductor or photovoltaic applications. These fundamental differences explain why high purity quartz sand (HPQ) has higher market value and requires specialized processing techniques.
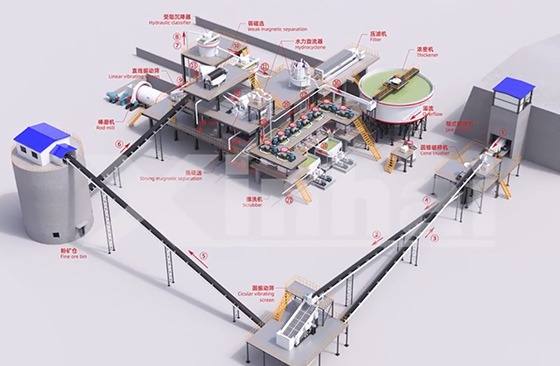
The purification of high purity quartz sand is a complex physical and chemical process aimed at removing various impurities from quartz raw materials, mainly including mineral impurities (such as feldspar, mica, ilmenite, etc.), fluid inclusions (gas-liquid inclusions), and substitutional/crystal lattice impurities. The entire process flow can be divided into the following key steps:
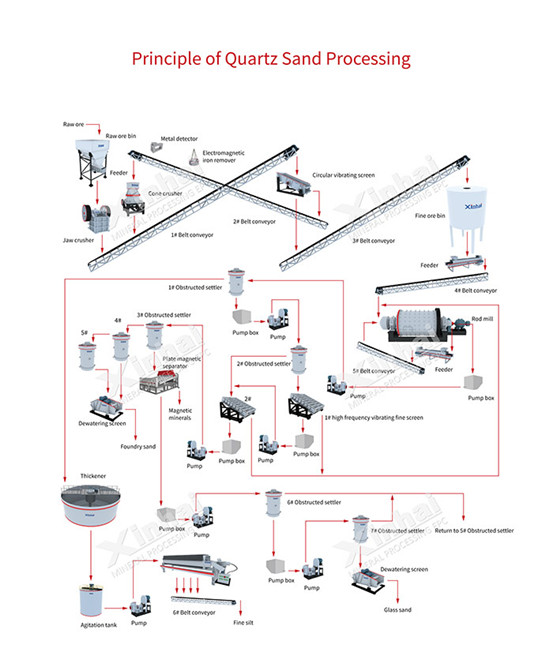
1. Raw Material Pretreatment and Beneficiation
First, we select high-quality raw ore, remove obvious large impurities manually or using optical sorters, and then crush and grind the ore to an appropriate particle size. During this process, special attention must be paid to avoiding the introduction of new metallic impurities such as iron. Subsequently, through sieving and classification, the particle size is precisely controlled, and finally, scrubbing is used to remove iron and argillaceous impurities from the surface.

2. Heat Treatment (Calcination)
High-temperature calcination, approximately between 900 and 1000 degrees Celsius, can decompose hydroxides and organic matter, while opening some gas-liquid inclusions enclosed in quartz. This step prepares for subsequent acid leaching and improves purification efficiency.
3. Acid Leaching and Chemical Purification (Core Step)
This is a critical link in removing metallic impurities. Different acids are used in stages:
Hydrochloric acid is used to remove feldspar, mica, and alkaline earth metal impurities;
Hot sulfuric acid effectively removes oxides such as iron, titanium, and aluminum;
Hydrofluoric acid can penetrate the crystal lattice or inclusions to completely remove refractory metallic impurities;
Sometimes, mixed acid synergistic treatment is adopted for more comprehensive results.
4. Deep Purification and Surface Treatment
For electronic-grade or photovoltaic-grade quartz sand, more refined treatment is required. Flotation is used to remove specific impurity minerals, ultrasonic cleaning is employed to penetrate tiny pores, and even hydrothermal synthesis or chemical vapor deposition is utilized to regrow quartz crystals to achieve extremely high purity.
5. Post-Treatment
After acid leaching, magnetic separation and flotation are performed again to remove potential secondary impurities. Subsequently, dehydration and drying are carried out, packaging is done in a clean environment, and strict quality testing is conducted to ensure that each batch of products meets high standards.
From an engineering perspective, each ore deposit requires a customized process solution. Xinhai Mining has accumulated rich experience in high purity quartz sand purification through laboratory testing, pilot-scale verification, and integrated process design, enabling stable impurity control under complex ore conditions.
The primary uses of high purity quartz sand span critical sectors like specialty lighting, semiconductors, LED production, optical fiber, photovoltaics (PV), and advanced electronic materials. In semiconductor manufacturing, it is essential for wafer processing and crystal growth, guaranteeing performance and precise process control. It also serves as a filler in copper-clad laminates and semiconductor-grade epoxy molding compounds. As fused silica glass, HPQ is used in halogen lamps.

The expansion of 5G, AI, and edge computing, leading to increased wafer output, continuously drives demand. Concurrently, the renewable energy boom fuels solar-grade polysilicon production, with significant HPQ required per gigawatt of solar panel capacity. Furthermore, HPQ shows growing potential in emerging applications like modern data center interconnects, UVC germicidal lamps, cryostat windows for quantum computing, and high-temperature aerospace ceramics, offering new avenues for market growth.
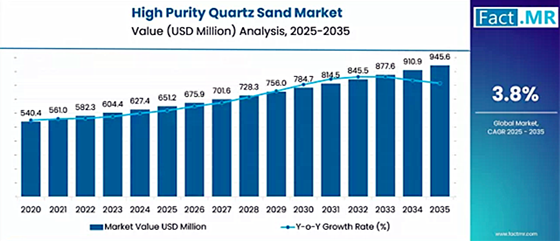
Driven by escalating demand for high-performance materials in advanced applications like semiconductors and solar panels, the global High Purity Quartz Sand market is projected to grow from USD 651.2 million in 2025 to USD 945.6 million by 2035, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8%.
1. Regional Distribution and Market Dynamics
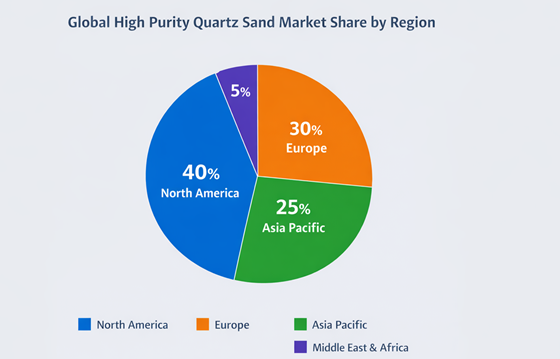
The global HPQ market continues to expand, primarily driven by technological progress and the energy transition. Rapid growth in semiconductor fabrication capacity and PV installations significantly boosts demand for high-quality HPQ. The Asia-Pacific region has become the fastest-growing consumption area, fueled by massive electronics manufacturing and solar investments. North America and Europe, with their mature processing technologies, remain key suppliers of premium HPQ. Market projections indicate stable growth over the next decade, with increasing focus on supply stability and quality consistency.
2. Challenges and Market Drivers
Beyond sustained demand, the market is shaped by broader trends. Global economic conditions and environmental regulations significantly influence the sector. Manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, driving innovation in extraction and processing methods. This shift towards environmentally conscious practices aligns with policy and appeals to eco-aware consumers and businesses. Simultaneously, the global focus on renewable energy further propels market growth, as HPQ is a core material in PV cell manufacturing. Continuous R&D investment and emerging applications present significant growth potential and opportunities.
3. Comparison Between High Purity Quartz Sand from Different Regions
HPQ resources and processing capabilities vary significantly by region. North America is renowned for high-grade quartz deposits and advanced purification technologies, supplying premium products for high-end markets. European producers focus on precision processing and rigorous quality control, often serving specific application niches. In the Asia-Pacific region, burgeoning demand has accelerated investment in beneficiation and purification technologies, gradually enhancing product quality and supply capacity. These regional differences impact the global market's cost structures, product consistency, and long-term supply reliability, a key consideration for any comprehensive high purity quartz sand market analysis.
Conclusion
From engineering and mineral processing perspectives, the High Purity Quartz Sand market is defined by technological capability, not just resource volume. Stable HPQ production requires in-depth knowledge of mineralogy, integrated process design, and contamination control throughout the entire beneficiation chain.
As a mining EPC+M+O service provider with rich experience in complex mineral processing projects, Xinhai Mining specializes in delivering customized purification solutions, supported by laboratory testing, pilot-scale verification, and full-cycle engineering design. This integrated approach ensures that HPQ projects achieve reliable product quality and maintain operational efficiency in an increasingly competitive global market, navigating the evolving high purity quartz sand market trends.
Share your project details and our engineers will get back to you shortly.