
Haematite is a weakly magnetic iron mineral with 70% pure iron content and good flotability. It is one of the main raw materials for iron making. There are many commonly used haematite extraction processes, which mainly include gravity separation, flotation separation, magnetic separation, roasting-magnetic separation, and combined separation. This article will teach you how to extract iron from haematite.
Gravity separation of haematite mainly includes two types: coarse-grained gravity separation and fine-grained gravity separation. They are suitable for separating coarse-grained (20mm-2mm) and medium-grained haematite ore.
1. Coarse-grained gravity separation
The geological grade of the haematite deposit is high, but the ore body is thin. It has many interlayers, and waste rock is easy to mix in, leading to ore dilution. For this situation, only crushing without grinding is adopted. Coarse-grained hematite is separated by the gravity separation to discard coarse-grained tailings to restore the geological grade.
2. Fine-grained gravity separation
After being crushed, the fine-grained haematite is separated by grinding and then processed by gravity separation to obtain fine-grained high-grade concentrate. As the grade of hematite is generally not high, the gravity separation process has a low unit processing capacity, so gravity separation is usually used in a combined process to improve the concentrate grade.

Flotation separation of haematite mainly includes obverse flotation separation and reverse flotation separation, which are suitable for the separation of fine-grained and micro-fine grained hematite.
1. Obverse flotation separation
Obverse flotation separation is to use anionic collectors to separate iron minerals from the raw ore, and can directly discard coarse-grained tailings without desliming. The commonly used collectors include fatty acid collectors, alkyl sulfates and petroleum sulfonates, etc.

2. Reverse flotation separation
Reverse flotation separation is to use anionic or cationic collectors to separate gangue minerals from the raw ore. The anionic collector uses fatty acids activated by calcium ions. By sodium hydroxide or mixing it with sodium carbonate, the pH can be adjusted to more than 11, and then it adds starch, sulfonated lignin, and dextrin to inhibit iron minerals.
Reverse flotation separation with cationic collectors is to adjust the slurry to pH=8-9 with the help of sodium carbonate, and add starch, dextrin, tannin, etc. to inhibit iron minerals, and adopt amine collectors during reverse flotation. As collectors, ether amine is the first choice, followed by fatty amine.

Magnetic separation of haematite mostly adopts weak - strong magnetic separation, which is suitable for the separation of magnet-haematite mixed ore. The common haematite weak magnetic-strong magnetic separation process is that after being concentrated, tailings with weak magnetic separation is subjected to strong magnetic roughing and scavenging. The coarse concentrate with strong magnetic enters the strong magnetic separator for concentration.
Some of the strong magnetic minerals in haematite ore can easily cause blockage of the strong magnetic separator. So if the weak magnetic-strong magnetic separation process is used, it is often necessary to increase the weak magnetic separation operation before the strong magnetic separation operation to remove or separate the strong magnetic minerals in the ore.

Roasting-magnetic separation of haematite is generally applicable to hematite with fine grain size, low content of useful elements and low content of harmful elements. The haematite extraction process requires the ore to be magnetized and roasted to convert the haematite or martite into magnetite, and then separate them by the magnetic separator with a weak magnetic field.
Generally, in order to further improve the grade of iron concentrate, fine screening -regrinding - re-selection (concentrate grade can reach more than 65%) and re-grinding-reverse flotation (concentrate grade can reach 66%) and other methods to reprocess the iron ore concentrate derived from magnetic separation.

If the composition of haematite is complex and it is difficult to obtain a good separation index by using other processing processes, a combined processing process can be used. Commonly used haematite combined extraction processes are as follows:
1. Weak magnetic-gravity-reverse flotation process
This method is to screen out most of the higher quality primary ore from the raw hematite ore by weak magnetic separation or gravity separation. The remaining ore with difficult separation is processed by reverse flotation. This process can greatly reduce the amount of ore by reverse flotation. Besides, advantages of this process are obvious. For example, it has good combination and adaptability, the equipment has a high raw ore processing capacity, the parameter adjustment of equipment is more flexible, the electricity consumption and water consumption are relatively low. It can effectively reduce the production cost of the entire processing process and obtain greater economic benefits.

2. Strong magnetic-reverse flotation process
This method is to first recover fine-particle iron minerals through strong magnetic separation, which plays the dual role of desliming and discarding tailings, and creates better conditions for flotation; and then use reverse flotation for separation. The reverse flotation process is simple to use reagents, which can significantly reduce the entry of organic substances such as flotation reagents into the slurry and reduce its adverse effects on the flotation process.
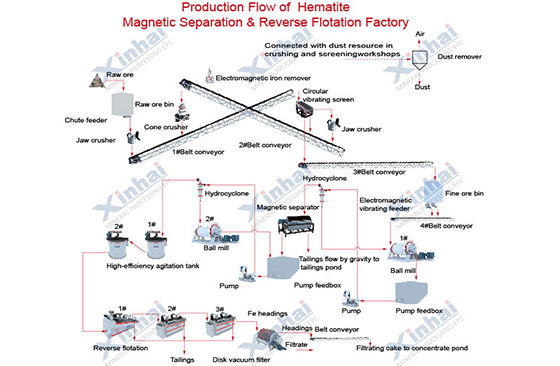
3. Strong magnetic-reverse flotation-roasting combined process
This method is to first obtain haematite concentrate with low impurity content through strong magnetic-reverse flotation, and then greatly improve the iron grade through ordinary roasting or production of pellet ore. Compared with other combined processes, the strong magnetic-reverse flotation-roasting combined process has lower production costs and facilitates good economic benefits.
To Wrap Up
The above are 5 methods for extraction of iron from haematite. According to different forms, haematite can be subdivided into several different ore types. In order to get the appropriate process for different haematite ore and realize the unification of economic and environmental benefits, it's recommended to have the processing test first, and a reasonable extraction process should be formulated according to the nature of the ore.
Share your project details and our engineers will get back to you shortly.