
Among many minerals, lead and zinc ores are difficult to be separated. And totally, lead and zinc have poor mines more than rich mines and with the complicated component. It is an important topic to research how to separate lead and zinc ore in high efficiency.
Now, the lead and zinc minerals which can be used for the industry are mainly galena, blende, and bonamite, cerusite and so on. According to the degree of oxidation, lead and zinc minerals can be classified into sulphide lead and zinc ores, oxidized lead and zinc ores, and mixed lead and zinc ores. We will analysis the processing technology from the degree of oxidation.
Compared with oxidized lead and zinc ores, sulphide lead and zinc ores are more easily to be processed. Sulphide lead and zinc ores include galena, blende, pyrite and copper pyrite. The main gangue minerals include calcspar, quartz, mica, dolomite, chlorite and so on. So one-block grinding or several-block grinding can be chosen in grinding stage, according to the growth relationship of lead and zinc minerals.
One-block grinding is usually used in dealing with sulphide lead and zinc minerals in more coarse fineness or simple growth relationship.
Several-block grinding is usually used in dealing with complex growth relationship and fine fineness.
Tailings regrinding and coarse concentration regrinding are commonly used rather than midding regrinding for sulphide lead and zinc ores.

In the separation stage, the flotation process is often used. At present, there are many flotation processes including preferential flotation process, mixed flotation process and so on. In addition, on the basis of the conventional direct flotation process, flotation process flow, separation process flow, branch and serial flow, etc. are developed, which are mainly selected according to their different granularity and nesting relationship.
Among them, due to the flotation of refractory ore and easy ore separation process and less chemical consumption, the flotation of lead and zinc sulfide ore process has certain advantages, especially in the presence of two kinds of lead and zinc minerals floating easily and difficult to float, such flotation process is a more appropriate choice.
The reason why oxidized lead and zinc ores are difficult to separate than sulphide lead and zinc ore is the complex component, unstable associated components, fine fineness, similar flotation characteristic, mud and soluble salt in it.
Among the oxidized lead and zinc ores, there are white lead ore (PbCO3), lead alum (PbSO4), zinc turpentine (ZnCO3), heteropolar ore (Zn4(H2O)[Si2O7](OH)2), etc.
Among them, white lead ore, lead alum and molybdenum lead ore are easy to be vulcanized, and can be vulcanized with sodium sulfide, calcium sulfide, sodium sulfide and other vulcanizing agents, but lead alum needs relatively long contact time in the vulcanizing process, and the amount of vulcanizing agent is relatively large.However, arsenic lead ore, chromium lead ore and phosphor-chlorine lead ore are difficult to vulcanize and have poor floatability.

For lead-zinc oxide ore, the priority flotation process is generally selected as the main separation process, and the desilting operation is carried out before flotation to improve the flotation index and dosage. In the selection of agents, long-chain xanthate is a common effective collector.It can also be replaced by secondary octyl yellow or no. 25 black according to different test results. But oleic acid, oxidized paraffin soap and other fatty acid collectors, its selectivity is poor, only suitable for silicate as the main gangue of high-grade lead ore.
It adopts the process of "coarse grinding and removal of the tail, multi-stage grinding and separation, and concentrated return of the middle ore", two sections of a closed-circuit crushing process, a section of the closed-circuit grinding classification process, and a coarse two-sweep, ten times of fine flotation process. The yield was 14.20%, the fixed carbon content was 92.30%, and the recovery rate was 87.91%. The final recovery rate was 92%.
Generally, mixed lead-zinc ore is separated by mixed-partial flotation process or mixed-priority flotation process, which successively separates oxide lead-zinc ore, lead concentrate and zinc concentrate. Of course, different areas of ore, the flotation order will be different, need to be determined through the ore processing test

Above are some of the simpler lead-zinc mine separating process description, here to remind you the mine owner, this conclusion is in ideal conditions to get the process, in the process of construction of dressing plant, there are many factors that need to consider, you need to consider factors such as economic condition, operating life, suggest to choose suppliers of experiment with beneficiation test certificate, and then make a decision of lead-zinc mine factory scale and specific ore dressing process flow.
Tibet 2400t/d lead-zinc processing plant design

Ore Characteristic:
Above are some of the simpler lead-zinc mine separating process description, here to remind you the mine owner, this conclusion is in ideal conditions to get the process, in the process of construction of dressing plant, there are many factors that need to consider, you need to consider factors such as economic condition, operating life, suggest to choose suppliers of experiment with beneficiation test certificate, and then make a decision of lead-zinc mine factory scale and specific ore dressing process flow.
Xinhai Solution:
With the preferential flotation process and reasonable chemical agent system, two kinds of products, lead concentrate and zinc concentrate, are obtained, and the silver mineral is concentrated in lead concentrate as much as possible.
Inner Mongolia 2000t/d lead-zinc ore processing plant project

Ore Characteristic:
The main metallic minerals of the project are pyrite, sphalerite, galena, etc. Nonmetallic minerals are mainly quartz, plagioclase, sericite, chlorite, Muscovite, etc. The lead content is about 2.0% and zinc is about 2.20%. The valuable elements are lead, zinc, gold and silver.
Xinhai solution:
In the first stage of grinding, fineness of -200mm accounts for 65%, and the lead is selected first. One coarse and two sweeps are used to select lead, and the lead coarse concentrate is then ground, and the fineness of grinding is -400mm accounts for 87%. Lead tailings are selected for zinc, and zinc is selected with one coarse, two sweeps and three times of selection to obtain the final zinc concentrate. All intermediate ores are returned to the flotation process in sequence.
Tibet 1600t/d lead and zinc processing plant design

Ore Characteristic:
The ore of this project is mainly characterized by the assemblage of lead-antimony-zinc minerals.Lead 4.12%, antimony 3.71%, zinc 1.74%.
Xinhai solution:
Two kinds of products, lead-antimony mixed concentrate and zinc concentrate, were obtained by using the technical process of lead-antimony preferential flotation and zinc-sulfur mixed flotation.
Study on beneficiation of oxidized lead-zinc ore in Shandong province
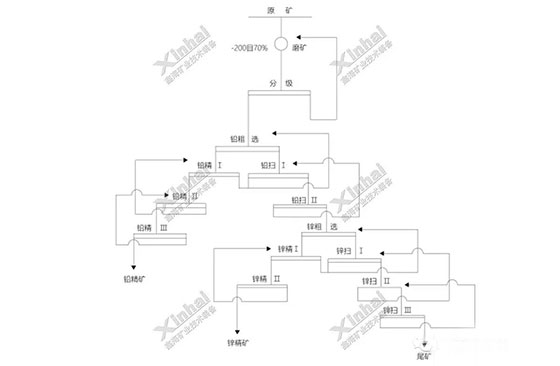
Ore Characteristic:
The raw ore of this project contains 6.90% lead, 28.81% zinc and 107.1g/t silver. The lead and zinc mineral contain both sulfide and oxidized minerals, which is a mixed refractory ore of multiple metals.The main lead and zinc minerals are galena, white lead, zinc blende, heteropolar and zinc calamine.
Xinhai solution:
The process of sulfur followed by oxygen, and the preferential flotation process can make the lead and zinc get better recovery, enrichment and separation, and effectively recover silver minerals.
To find out more about our products and solutions, please fill out the form below and one of our experts will get back to you shortly.