
Copper metal is one of the earliest metals used by human beings in history. It has excellent performance and widely used in power electronics, light industry, machinery, construction, transportation and other fields. With the continuous development of the economy, the demand for the copper metal is also growing. In order to meet the increasing demand, how to obtain more copper production from the limited copper resources and improve the efficiency of copper extraction has aroused people's attention.
Selecting the suitable ore dressing process is one of the necessary conditions for the high-efficient operation of the mineral processing plant. In order to obtain high yield copper and improve the efficiency of mineral processing, we need to choose the ideal copper extraction process. So how much do you know about the copper extraction process?
Due to the different types of copper ore, the nature of the copper ore is different, so the copper extraction process needs to be tailored. The selection of copper extraction process mainly depends on the composition of raw copper ores extracted from the mine, the structure and the occurrence state of copper (including the carrier minerals of copper, distribution rate and the grain size distribution of copper minerals).
Generally speaking, copper ore can be divided into three classifications: copper sulfide ore, copper oxide ore and natural copper ore.
● Copper sulfide ore: chalcopyrite, porphyry and pyroxene, etc.
● Copper oxide ore: red copper ore, malachite, azurite and silica malachite, etc.
● Natural copper ore: the content of copper in copper ore is about 1%. Generally, the minimum industrial grade of copper is 0.4%-0.5%.
According to the different physical and chemical properties of minerals in the copper ore, the copper extraction process means to combine one or several joint separation processes to separate useful minerals and gangue minerals after crushing and grinding, and then make all kinds of useful mineral symbiosis separate as soon as possible, then remove or reduc e the harmful impurities to obtain the copper metal that other industry needed for smelting.
For the copper extraction process, here are the specific explanation about copper sulfide ore and copper oxide ore:
Copper sulfide ore

1. Before copper extraction:
The massive sulfide ore is crushed to about 12cm by jaw crusher or cone crusher. This process may adopt multiple crushing stages, which needs to cooperate with the vibrating screen.
The qualified crushing materials are sent to the grinding mill through auxiliary equipment, such as conveyor and feeder. The material, water and steel balls in the grinding mill are ground and hit with each other, so the ore particles are further reduced, and the particle size of copper ore is decreased to 0.2-0.15cm finally.
2. Copper extraction:
The copper extraction stage is the key stage to improve the grade of copper ore. The pulp discharged from the grinding mill is transported to the agitation tank, where the flotation reagent is added in rouging flotation stage. After full agitation and activation of the agitation tank, the pulp is fed to the flotation cell.
Adding the collecting agent, adjusting agent and foaming agent during the flotation process, and the useful minerals are concentrated in the froth, which is scraped by the scraper of the flotation cell and then sent to the dewatering machine.
3. After copper extraction:
The enriched pulp obtained in the flotation workshop is concentrated and dewatered by mechanical dewatering, and then transported to the smelter for smelting. Finally, the grade of copper is up to 99.0%-99.7%.
Copper oxide ore
There are two kinds of common copper oxide ore extraction processes: flotation process and leaching process, so the extraction processes are different.
1. Flotation process

● Before copper extraction:
Same as the copper sulfide ore.
● Copper extraction:
The flotation process is also suitable for oxidizing ore, the difference lies in the selected flotation reagents. According to the flotation reagents used, there are five common flotation processes: sulphide flotation process, fatty acid flotation process, amine flotation process, emulsion flotation process and chelate-neutral oil flotation process.
● After copper extraction:
Same as the copper sulfide ore.
2. Leaching process
The common leaching processes of copper oxidized ore include heap leaching, pool leaching, in-situ leaching and agitation leaching.

The mined ore is crushed to a certain size by the crusher. Because the leaching stage does not need to reach the same small particle size as the flotation process, the heap leaching process does not need grinding stage, the ore can be directly sent to heap leaching after crushing. The oxide ore (mix with partial sulfide ore) is placed on a leaching pad and sprayed with the strong acid solution to permeate the crushed ore. As time goes on, the copper in the crushed ore is leached into the solution as the pregnant solution, and then pumped to solvent extraction equipment for further purification.
● Pool leaching
The pool leaching process is a common leaching method used in early wet copper smelting. Using the strong sulfuric acid solution to leach the 1-2% copper-contained oxidized ore (particle size is -1cm). Because the concentration of copper in the leach solution is high, it can be directly used for the copper electrodeposition.
● In-situ leaching process
During in-situ leaching, the well spacing is generally 30x30cm (or 15×7.5m), and the diameter of the borehole is 15-25cm. Plastic pipe is set in the hole through the ore body, and the leaching agent flows into the ore body along the plastic pipe, the leaching solution is pumped back to the ground from the bottom of the ore body.
In-situ leaching process can be used to treat the residual ore of old mines or the unmined oxidized copper ore and lean copper ore. In-situ leaching process has better potential than other processes for those abandoned mines or uneconomical copper mines with other processes.
● Agitation leaching process
Agitation is carried out in the leaching tank equipped in the agitation leaching device. The fine grains (-75um accounts for 90%) oxidized ore or calcined sulfide ore are leached by high concentrated sulfuric acid solution. There are two ways of leaching: air agitation and mechanical agitation.
Because of small particle size and sufficient agitation, agitation leaching process has faster leaching speed and higher recovery rate than pool leaching process. Therefore, agitation leaching process can treat high-graded ore or the ore with lower-graded tailings (Cu < 1%).
Summary:
In the actual mineral processing, the selection of copper extraction process is often determined by the properties of copper ore, mineral processing conditions, investment budget and other factors. It is suggested that the copper ore shall be first understood before select the copper extraction process, then and the single or combined copper extraction process shall be selected according to the mineral processing indexes so as to strive for the ideal technical and economic benefits.
1. Mexico 1500tpd polymetallic ore project

Ore properties: Copper, lead, zinc and silver minerals were mainly associated with sulfide ore and oxidation ore.
Xinhai solution: Three-stage crushing with single closed-circuit stage – two-stage grinding – bulk and separating flotation – two stage dewatering process. The recovery rate of copper ore reached 83.30%.
2. Columbia 1000tpd copper ore project
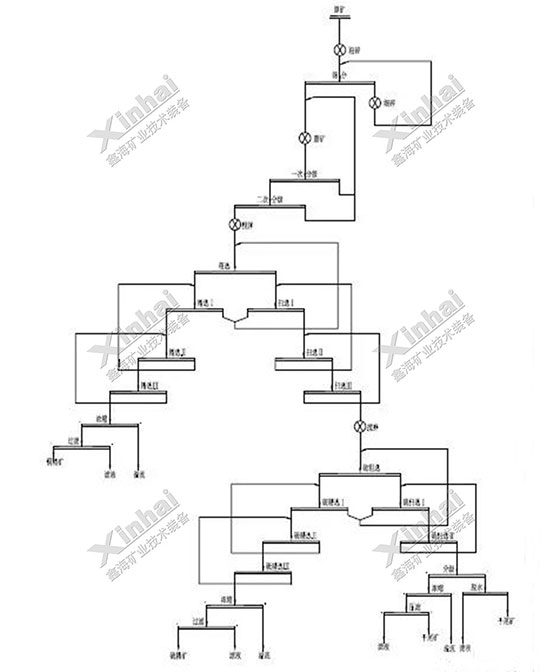
Ore properties: The most common copper was oxidation ore, and a small number of sulfide ore. In the future, the most common copper will be sulfide ore, the oxidation ore will account for a small number.
Xinhai solution: Single flotation process. After the grinding stage, the sulfide ore was processed by one roughing, two scavengings, the oxidized ore was processed by one roughing, three scavenging and two cleaning, and finally the productive rate of mixed concentrate was 30%, the grade of copper concentrate was 25.95%, and the recovery rate was 87.15%.
3. Peru 550tpd copper ore project

Ore properties: The main metal minerals in the project were chalcopyrite and porphyry, followed by magnetite and pyrite. Gangue mineral was calcite.
Xinhai solution: Two-stage crushing with single closed-circuit stage – one stage closed-circuit grinding stage - rapid flotation for recovering the coarse copper ore, one roughing, three scavengings, four cleaning for recovering the fine copper ore, tailings cleaning for obtaining the sulfur concentrate, two stages magnetic separation of copper flotation tailing for obtaining iron concentrate.
4. Yunnan 1000tpd copper ore project

Ore properties: Copper
Xinhai solution: Two stages crushing with single closed-circuit stage - one stage closed-circuit grinding and classification - one roughing, three scavenging and three cleaning flotation - concentration and filtration two stages of dewatering process.
5. Philippines 200tpd copper ore project
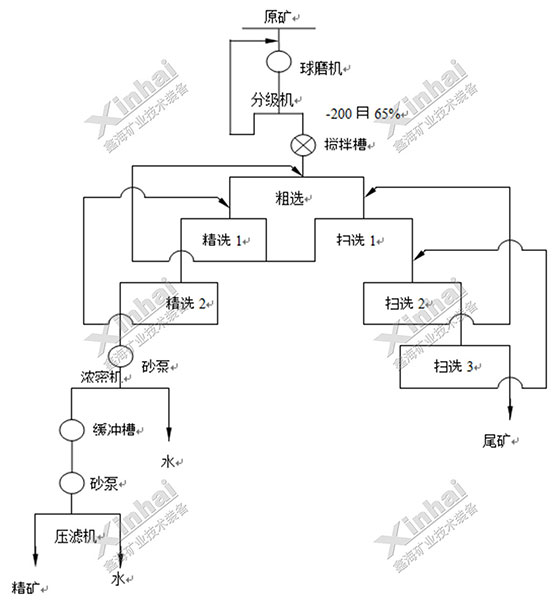
Ore properties: The main metal minerals were chalcopyrite, pyrite, malachite, copper blue, limonite and sphalerite.
Xinhai solution: Two-stage crushing with single closed-circuit stage – one stage closed-circuit grinding and classification – one roughing, three scavengings, two cleaning flotation process. The grade of copper was 7.0%, the grade of copper concentrate was 26.5%, the rate of copper concentrate was 25.1%, and the recovery rate was 95.0%.
To find out more about our products and solutions, please fill out the form below and one of our experts will get back to you shortly.