
Cyanidation has a history of more than 200 years since it was applied to gold and silver ore extraction in 1887. At present, cyanidation is still one of the main gold extraction process due to its high recovery rate, high adaptability to ore and local production.
Generally, cyanidation methods can be divided into two categories: agitation cyanidation and percolation cyanidation. Among them, agitation cyanidation is mainly used to treat flotation gold concentrate or all-slime cyanidation. Percolation cyanidation is mainly applied in dealing with low-graded gold ores.
Agitation cyanidation gold extraction process mainly includes two kinds of gold extraction processes. One is the cyanidation-zinc replacement process (CCD method and CCF method) which uses the zinc powder (silk) to replace and recover the gold after the continuous countercurrent washing. Another is the unfiltered cyanidation carbon slurry process (CIP method and CIL method), which adopts the activated carbon to absorb and recover the gold directly from the cyanidation pulp without filtration and washing.
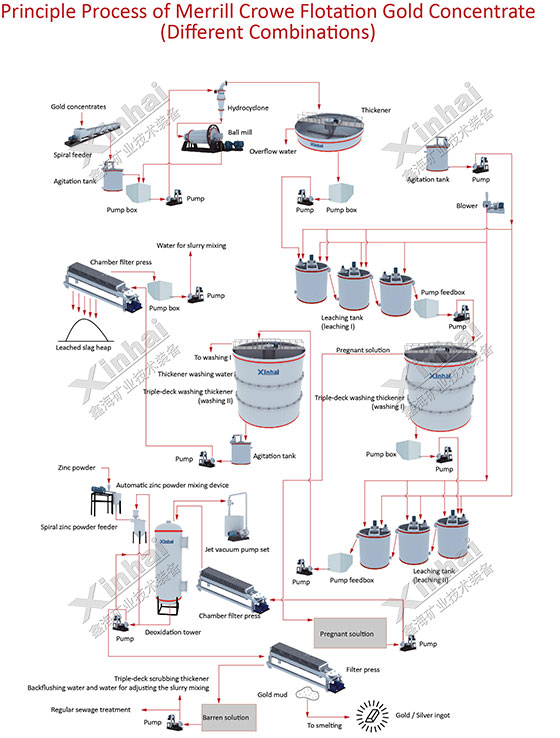
1. Cyanidation-zinc replacement process
Cyanidation-zinc replacement process (CCD method and CCF method) mainly includes the following steps: the preparation of leaching raw materials, agitation cyanidation leaching, countercurrent washing for solid-liquid separation, the purification of leaching liquid and deoxidation, zinc powder (silk) replacement and pickling, smelting ingots.
2. Cyanidation carbon in pulp process
Carbon pulp extraction process (CIP method and CIL method) is to put activated carbon into the cyanidation pulp, and the dissolved gold is adsorbed on the activated carbon, then the gold is extracted from the activated carbon. This process mainly includes the following steps: the preparation of leaching materials, agitation leaching and countercurrent carbon adsorption, gold-loaded carbon desorption, electrowinning electrolysis, smelting ingots, carbon regeneration.
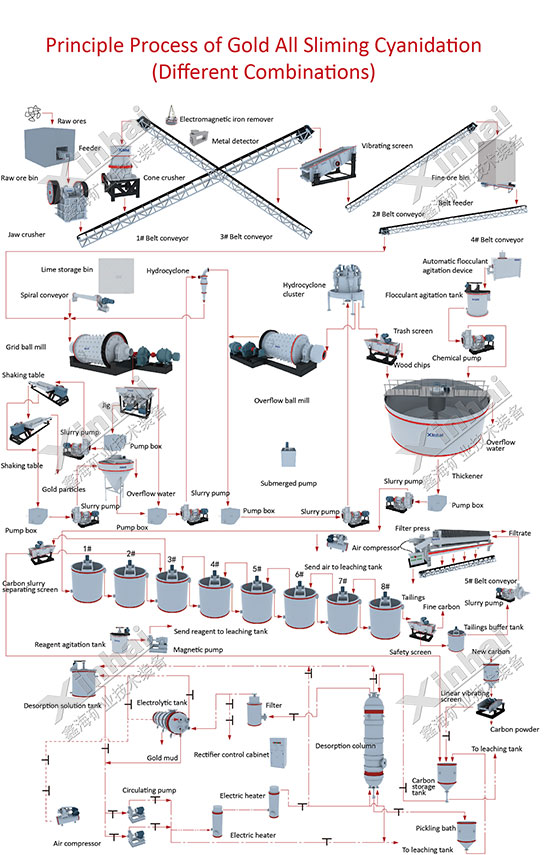
Carbon in pulp (CIP): Cyanidation leaching first, then add the activated carbon to adsorb the gold in the pulp;
Carbon in leaching (CIL): Add the activated carbon to the leaching tank, and the leaching and adsorption are carried out simultaneously.
In the CIP process, the leaching and adsorption are two independent operations. In the adsorption operation, the leaching process is basically completed, and the size, number and operation conditions of the leaching adsorption tank are determined by the adsorption parameters. In the CIL process, the leaching and adsorption are carried out simultaneously. In general, the leaching operation takes longer time than the adsorption operation, so the size, aeration and dosing of the tank are determined by the leaching parameters. Since the adsorption rate is a function of the dissolved gold concentration in the solution, add one or two levels of pre-leaching before leaching and absorption can increase the concentration of dissolved gold in the front adsorption tank and increase the leaching time.

Comparison between CIP and CIL:
1. The CIP process is longer than the CIL process, but there are a large amount of carbon and a low concentration of carbon in the CIL process, so the slurry volume for carbon transshipment in the CIL process is several times that of CIP (generally four times);
2. There is a large amount of metal backlog in the CIP process, and the distribution of metal backlog in the two processes is different. The distribution of the metal backlog in the CIP process on the activated carbon is basically the same as that in the solution, but in the CIL process, the metal is mainly deposited on the activated carbon. Besides, the amount of gold in the solution also varies.
3. The gold grade in the solution in the CIL process is higher than the CIP process, which is determined by the process structure. The CIL process is composed of leaching and adsorption at the same time. So, the new dissolved gold constantly enters the solution, the gold in the solution is constantly replenished and the gold content in the solution is relatively high. The CIP process is the single adsorption, the complementary quantity of dissolved gold in the solution is very small, so the gold grade is lower.

Percolation cyanidation process is also one of the cyanidation leaching processes. Based on the cyanidation solution permeating through the ore layer, the gold in the gold bearing ore can be leached, which is suitable for placer and porous materials.
There are two kinds of percolation cyanidation gold extraction processes: pool leaching and heap leaching. The leaching solution is percolated, then the activated carbon or zinc powder (silk) replacement is used to extract the gold.
1. Pool leaching
The percolation leaching is usually carried out in a leach tank, which usually includes wood tank, iron tank or cement tank. The bottom of the pool is horizontal or slightly inclined in a round, rectangular or square shape. The tank is equipped with a false bottom made of perforated acid-resistant plate, which is covered with a press cloth, and the press cloth is covered with the grid with wooden or corrosion-resistant metal strips. When leaching, the ore is placed in the pool, and the leaching agent is added above the pool, the leaching liquid flows out from the false bottom part. The false bottom is used to filter and support the ore.
The leaching time not only depends on the dissolution rate of mineral by solvent, but also depends on the permeability rate of solvent in the material layer. And the permeability rate mainly depends on the loading height, porosity, silt content, leaching agent viscosity and the material characteristics.
2. Heap leaching
The raw ore is transferred to the ore mining yard prepared in advance or the waste rock or low-grade ore, then the cyanide leaching liquid spray or infiltrate the ore, the solution produces the percolation leaching when it passing through the ore. After many time od leaching liquid cycling, repeat spray, the leachate is collected, then the activated carbon or zinc replacement is used to extract the gold, and the lean solution returns to the heap leaching for recycling.
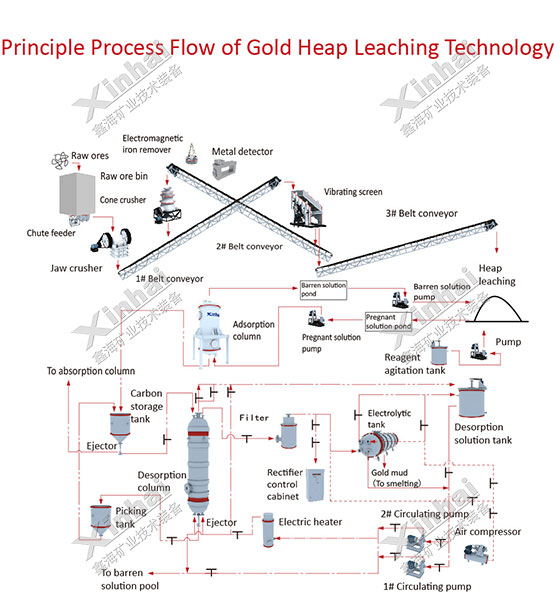
The heap leaching sites are usually located in the hilly areas with a gentle slope (natural gradient 5-15), which is close to the stope and convenient for transportation. Firstly, clean the weeds, floating soil and tamping, then build a foundation with a gradient of around 5˚, the height on both sides slightly lower in the middle, so that the leaching fluid can be concentrated into the storage tank. The storage yard is covered with a geotechnical film to prevent leakage. Soil banks of 0.4 meters are built around the yard and used as drains to prevent rainwater from flowing into the yard. A large lean ore with 0.3 m thick is deposited before the ore is piled.

The heap leaching method has low production cost and can be put into production quickly. Besides, the scale of heap leaching can be large or small, and the amount of ore in each heap can reach hundreds of tons. Heap leaching or granulation heap leaching can be used after ore crushing to a certain size.
Before selecting the specific process, it is suggested that each mine owner should do the ore dressing test in advance, determine the appropriate cyanidation process according to the results of the ore dressing test, and make a choice by combining the scale of the mineral processing plant, the conditions of the mineral processing plant, the investment cost and other factors, so as to achieve the best balance between the technical and economic indexes.
To find out more about our products and solutions, please fill out the form below and one of our experts will get back to you shortly.